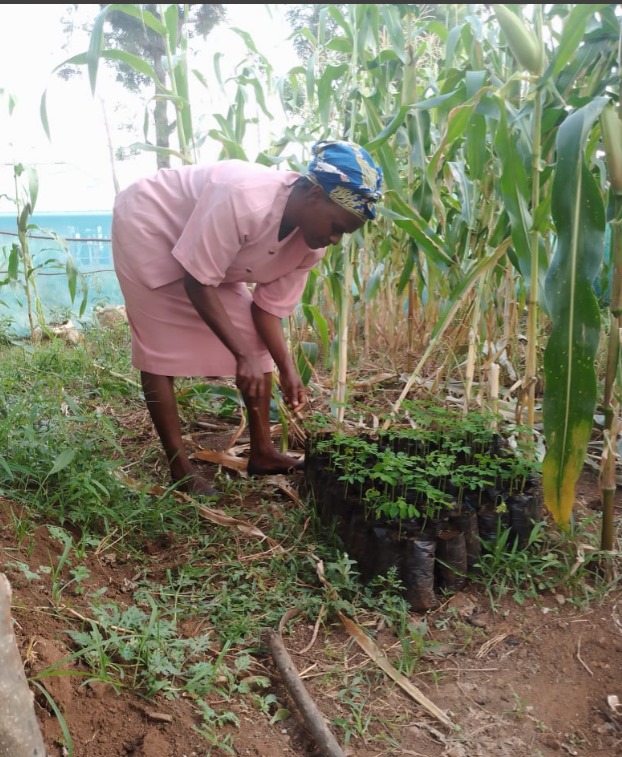
Moringa is a powerful ally in the fight against climate change due to its remarkable environmental benefits.
Here’s how Moringa contributes to climate resilience:
- Carbon Sequestration: Moringa trees absorb significant amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere, helping to reduce greenhouse gas concentrations. A single mature tree can capture up to 20 times more CO2 than most other trees, making it highly effective for carbon sequestration.
- Soil Restoration: Moringa improves soil quality by preventing erosion and enriching the soil with nutrients. Its deep roots stabilize the soil, while its fallen leaves add organic matter, enhancing soil fertility and promoting sustainable agriculture.
- Drought Resilience: Moringa thrives in arid and semi-arid conditions, making it ideal for regions affected by climate change. Its drought-tolerant nature helps farmers in vulnerable areas maintain productivity even during dry seasons, contributing to food security.
- Water Conservation: Moringa requires less water than many other crops, which is crucial for areas facing water scarcity due to climate change. It helps optimize water use, supporting sustainable farming practices.
- Agroforestry Integration: Moringa can be incorporated into agroforestry systems, promoting biodiversity and providing shade for other crops, thus improving overall ecosystem health and reducing the negative effects of monoculture farming.
By planting Moringa, we can tackle both environmental and socio-economic challenges, helping farmers adapt to climate change while protecting our planet.